G-LNS: Generative Large Neighborhood Search for LLM-Based Automatic Heuristic Design
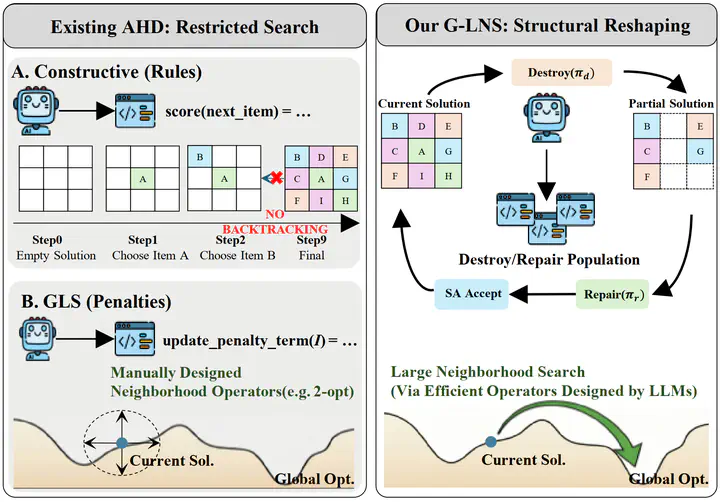 G-LNS framework: Synergy-aware co-evolution of destroy and repair operators for Large Neighborhood Search. The Synergy Matrix models operator interactions, enabling discovery of complementary pairs through dual-population evolutionary optimization.
G-LNS framework: Synergy-aware co-evolution of destroy and repair operators for Large Neighborhood Search. The Synergy Matrix models operator interactions, enabling discovery of complementary pairs through dual-population evolutionary optimization.Highlights
- First framework to co-evolve destroy and repair operators for Large Neighborhood Search using LLMs
- Synergy Matrix explicitly models operator interactions during evolutionary process
- Dual-population architecture maintains separate populations for destroy and repair operators
- Generative design produces executable code rather than just parameter tuning
- Strong generalization to unseen problem instances and distributions
- Near-optimal solutions on TSP and CVRP benchmarks with reduced computational budgets
Key Innovations
1. Synergy-Aware Co-evolution
Unlike previous methods that evolve heuristics independently, G-LNS explicitly captures complementary relationships between destroy and repair operators through a Synergy Matrix. This guides adaptive selection during evolution and enables discovery of operators that work together effectively.
2. Generative LNS Design
G-LNS generates executable Python code for LNS operators rather than restricting to predefined templates or parameter tuning. This enables true structural algorithmic innovation and discovery of novel operator combinations.
3. Dual-Population Evolution
Separate populations for destroy and repair operators evolve in parallel, with fitness evaluation based on paired performance. The Synergy Matrix guides crossover and mutation to produce complementary operator pairs.
4. Multi-Episode Evaluation
Robust fitness assessment through multi-episode testing on problem instances, reducing noise from stochastic LNS performance and ensuring discovered heuristics are consistently effective.
Applications
G-LNS is applicable to diverse combinatorial optimization domains:
- Routing Problems: TSP, CVRP, Vehicle Routing with Time Windows
- Scheduling: Job shop scheduling, flow shop scheduling
- Bin Packing: Multiple variants and extensions
- Graph Problems: Graph coloring, maximum clique
- Resource Allocation: Task assignment, facility location
Collaboration
This work represents collaborative research between:
- Northeastern University (Baoyun Zhao, Liang Zeng)
- University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (He Wang)
- Tsinghua University (Liang Zeng)
Resources
- Paper: arXiv:2602.08253
- Code: GitHub Repository (MIT License)
- Website: Project Homepage
- Project Page: G-LNS Project
For detailed technical information, installation instructions, and usage examples, please visit the project website or explore the GitHub repository.