Lecture 8. Deep Learning Hardware and Software
Table of Contents
CS231n 课程的官方地址:http://cs231n.stanford.edu/index.html
该笔记根据的视频课程版本是 Spring 2017(BiliBili),PPt 资源版本是 Spring 2018.
1. CPU vs GPU
GPU 占据很大的空间和能量
GPU 就选 NVIDIA 的,没的说。
GPU 和 CPU 之间有很多差异:
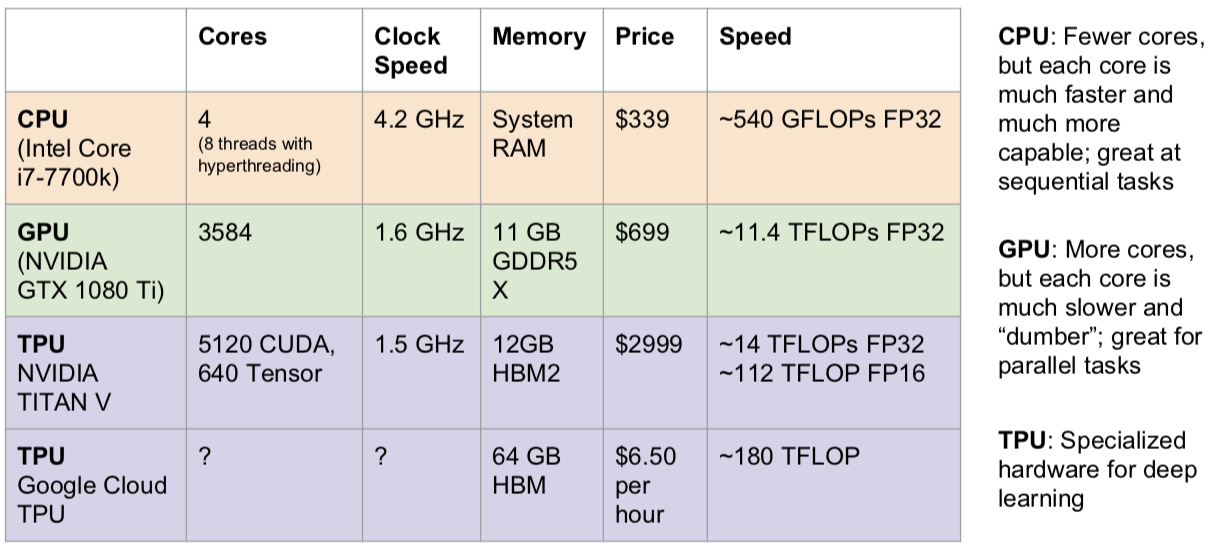
Note:TITAN V isn’t technically a “TPU” since that’s a Google term, but both have hardware specialized for deep learning
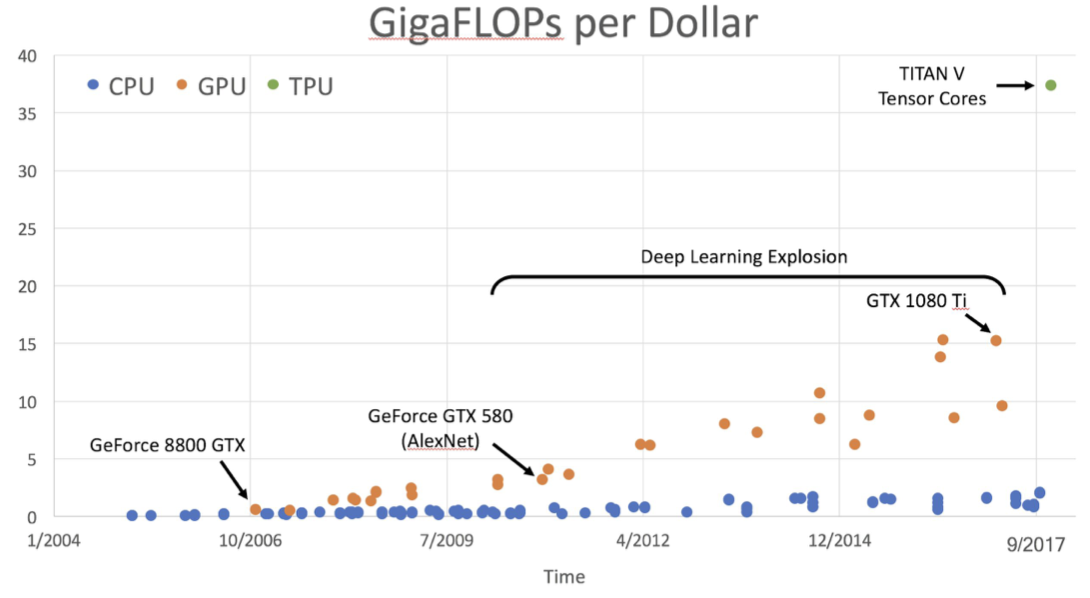
GPU 和 CPU 在价格上的差异变化:
在实际情况下,GPU 和 CPU 表现的差异:
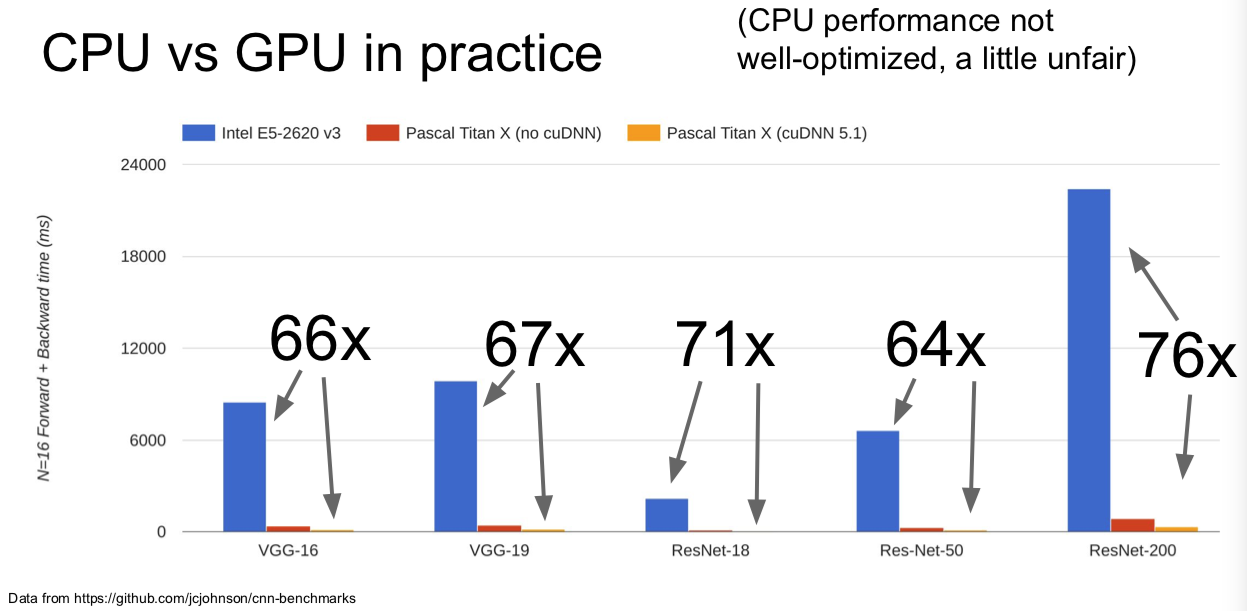
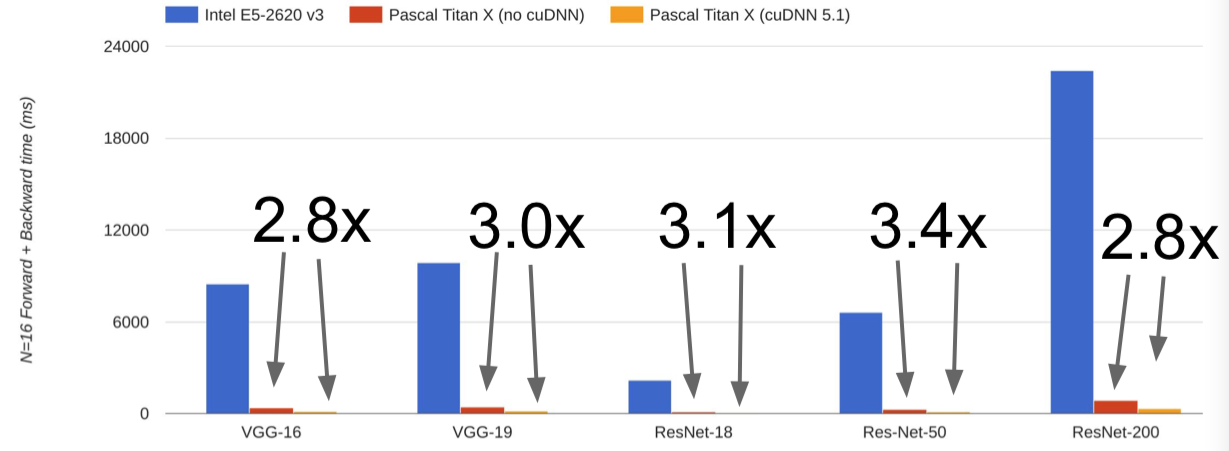
- cuDNN much faster that “unoptimized” CUDA
Programming GPUs
- CUDA(NVIDIA only)
- Write C-like code that runs directly on the GPU
- Optimized APIs:cuBLAS, cuFFT, cuDNN, etc
- OpenCL
- Similar to CUDA, but runs on anything
- Usually slower on NVIDIA hardware
- HIP https://github.com/ROCm-Developer-Tools/HIP
- New project that automatically converts CUDA code to something that can run on AMD GPUs
- Udacity:Intro to Parallel Programming https://www.udacity.com/course/cs344
- For deep learning just use existing libraries
- CUDA(NVIDIA only)
CPU / GPU Communication
- If you aren’t careful, training can bottleneck on reading data and transferring to GPU!
- Solutions:
- Read all data into RAM
- Use SSD instead of HDD
- Use multiple CPU threads to prefetch data.
小哥谈到,从软件上来说,可能你能做到的最有效的事情就是:设定好 CPU 的预读内容(pre-fetching),比如避免这种比较笨的序列化操作,你先把数据从硬盘里读出来,等待小批量的数据一批一批地读完,然后依次送到 GPU 上做正向和反向传播,再读下一个小批量的数据,按顺序这样做。如果你有多个CPU,比如说多个 CPU 线程在后台从硬盘中搬运出数据,这样的话,你可以把这些过程交错着运行起来。GPU 在运行的同时,CPU 的后台线程从硬盘中取数据,主线程等待这些工作完成,在它们之间做一些同步化,让整个流程并行起来。好在如果你使用了下面要讲到的这些深度学习框架,它们已经替你完成了这部分操作,因为实现起来有点麻烦。
2. Deep Learning Frameworks
- 第一代深度学习框架都是有学术界建立和维护起来的。
- 下一代深度学习框架全部由工业界产生。
- 使用深度学习框架的理由:
- Quick to develop and test new ideas
- Automatically compute gradients
- Run it all efficiently on GPU (wrap cuDNN, cuBLAS, etc)
I love MXNet!