G-LNS: Generative Large Neighborhood Search for LLM-Based Automatic Heuristic Design
 (Source: G-LNS)
(Source: G-LNS)🧬 Overview
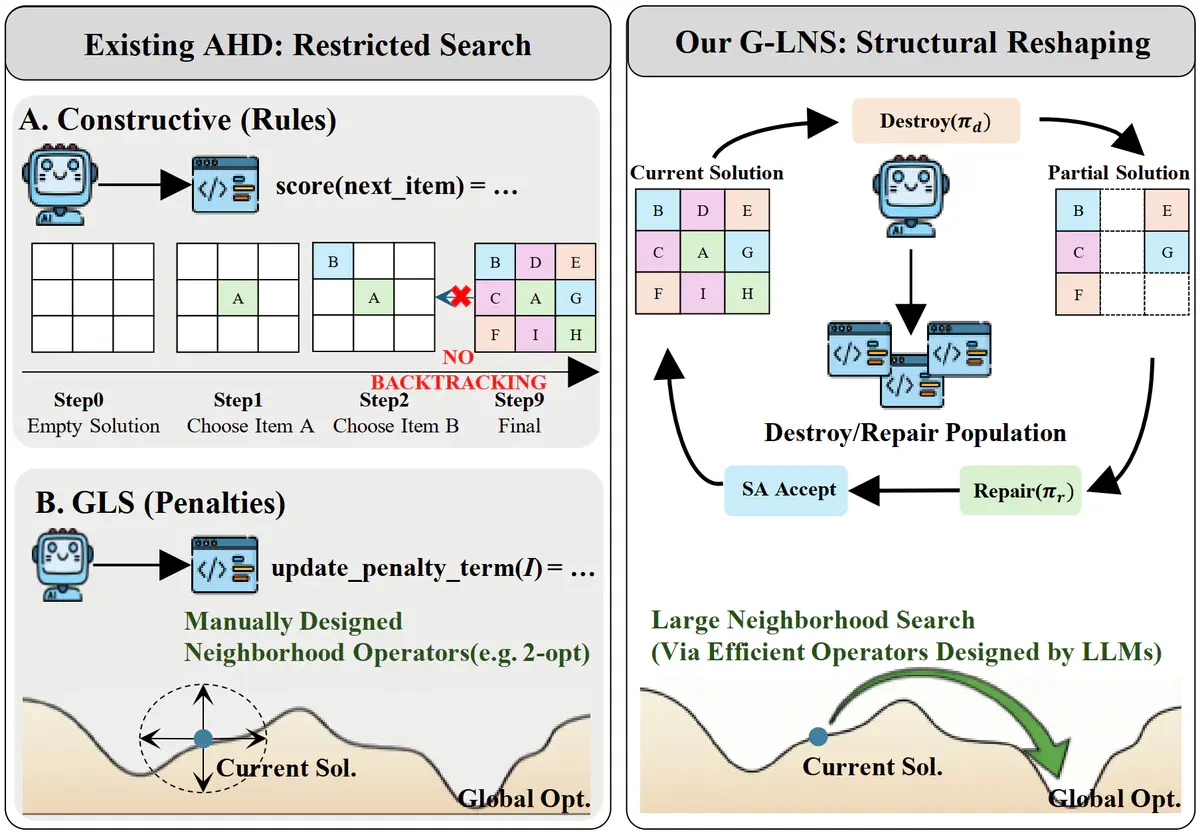
G-LNS (Generative Large Neighborhood Search) represents a breakthrough in automated algorithm design, leveraging Large Language Models to automatically create Large Neighborhood Search operators for combinatorial optimization problems. Unlike traditional approaches that restrict designs to fixed heuristic forms, G-LNS enables structural algorithmic innovation through the co-evolution of tightly coupled destroy and repair operator pairs.
Developed by researchers from Northeastern University, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Tsinghua University (Baoyun Zhao, He Wang, and Liang Zeng), this work demonstrates that LLMs can discover high-quality heuristics that achieve near-optimal solutions with reduced computational budgets while generalizing effectively across different problem instances.
As highlighted on the project website: “Give G-LNS domain expertise and LLM creativity, and get state-of-the-art optimization heuristics in return!”
🚀 Key Innovations
- Generative LNS Design: Generates executable code for operators rather than just parameter tuning, enabling structural algorithmic innovation
- Synergy-Aware Co-evolution: Explicitly models operator interactions through a Synergy Matrix during evolutionary process
- Dual-Population Architecture: Separate populations for destroy and repair operators that evolve through adaptive selection and crossover
- Robust Generalization: Discovered heuristics perform well across diverse and previously unseen problem distributions
- Multi-LLM Support: Compatible with various LLM providers including DeepSeek API
🔬 Technical Architecture
Core Components
- Initialization Phase: Seeds populations with domain expertise and LLM-generated operators
- Evaluation Engine: Adaptive LNS with multi-episode testing for robust fitness assessment
- Population Management: Fitness-based ranking and selection mechanisms
- Evolution Process: Combines mutation and crossover operations guided by synergy awareness
Synergy Matrix
The breakthrough innovation is the Synergy Matrix that explicitly captures how destroy and repair operators interact:
- Models complementary relationships between operator pairs
- Guides adaptive selection during the evolutionary process
- Enables discovery of operators that work together effectively
- Addresses limitations of previous methods that evolved heuristics independently
Operator Co-evolution Process
- Initialization: Generate initial operator populations using domain knowledge and LLMs
- Fitness Evaluation: Test operator pairs on problem instances with multi-episode sampling
- Synergy Assessment: Update matrix based on paired performance outcomes
- Selection: Choose promising operators weighted by synergy scores
- Crossover & Mutation: Create new operators through LLM-guided recombination
- Iteration: Repeat until convergence or computational budget exhausted
📈 Performance Results
G-LNS demonstrates exceptional performance on benchmark combinatorial optimization problems:
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP)
- Achieves near-optimal solutions on various TSP instances
- Reduced computational budget compared to traditional methods
- Strong generalization to problem sizes not seen during training
Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP)
- Discovers effective heuristics for complex routing scenarios
- Balances solution quality with computational efficiency
- Maintains robust performance across diverse problem distributions
Key Advantages
- Near-Optimal Solutions: Consistently produces high-quality results
- Computational Efficiency: Reduced budgets compared to exhaustive search
- Generalization: Transfers to unseen problem instances and distributions
- Interpretability: Generated heuristics are human-readable code
- Flexibility: Applicable to diverse combinatorial optimization domains
💻 Getting Started
Installation
git clone https://github.com/zboyn/G-LNS.git
cd G-LNS
pip install -r requirements.txt
Configuration
Create a .env file with your LLM API credentials:
DEEPSEEK_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
Running Examples
Traveling Salesman Problem:
python examples/tsp/run_tsp.py
Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem:
python examples/cvrp/run_cvrp.py
📂 Repository Structure
G-LNS/
├── base/ # Base classes and core framework
├── datasets/ # Dataset generation utilities
├── examples/ # Training scripts and examples
│ ├── tsp/ # TSP experiments
│ └── cvrp/ # CVRP experiments
├── heuristics/ # Discovered heuristics
├── problems/ # Problem definitions
└── utils/ # Utility tools and LLM API integration
🎯 Applications
G-LNS is applicable to a wide range of combinatorial optimization problems:
- Routing Problems: TSP, CVRP, Vehicle Routing with Time Windows
- Scheduling: Job shop scheduling, flow shop scheduling
- Bin Packing: Multiple variants and extensions
- Graph Problems: Graph coloring, maximum clique
- Other Domains: Any problem amenable to neighborhood search heuristics
🔗 Resources
- Paper: arXiv:2602.08253
- Hugging Face Papers: huggingface.co/papers/2602.08253
- Code: GitHub Repository
- Website: Project Homepage
- License: MIT License
📝 Citation
If you use G-LNS in your research, please cite:
@article{zhao2026glns,
title={G-LNS: Generative Large Neighborhood Search for LLM-Based Automatic Heuristic Design},
author={Zhao, Baoyun and Wang, He and Zeng, Liang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2602.08253},
year={2026}
}
🤝 Collaboration
This project represents collaborative research between:
- Northeastern University
- University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS)
- Tsinghua University
🌟 Future Directions
- Extension to additional combinatorial optimization problems
- Integration of multi-objective optimization capabilities
- Exploration of transfer learning across problem domains
- Development of adaptive computational budget allocation strategies
- Investigation of hybrid approaches combining G-LNS with other metaheuristics
Ready to revolutionize your optimization workflow? Visit the project website or explore the GitHub repository to get started!